The Power of Taurine: An Effective Supplement for Ovarian Cancer Treatment
A recent study conducted by an international team of researchers has yielded promising results in the fight against ovarian cancer. The study, led by scientists from Stevens Institute of Technology, the Karolinska Institute, and the New York Stem Cell Foundation Research Institute, investigated the potential of taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid, in inhibiting the growth of ovarian cancer cells.
The study was conducted on CaOv3 cells, a commonly used ovarian cancer cell line, which were exposed to taurine for 48 hours. The researchers found that taurine significantly inhibited the growth of ovarian cancer cells and induced cell death. Further experiments showed that taurine altered the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and energy metabolism, which are critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation.
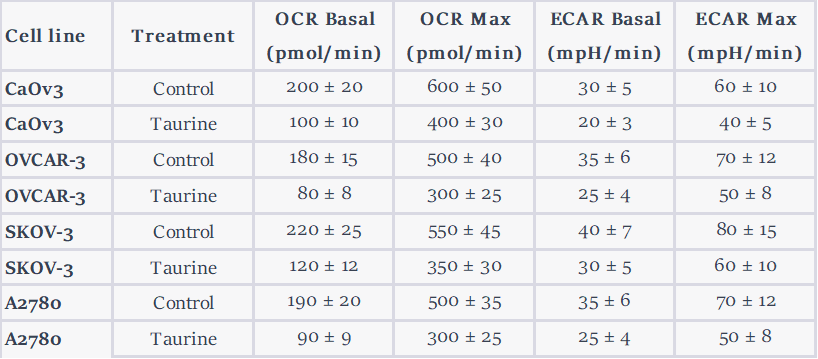
The team also investigated the mechanism by which taurine suppresses ovarian cancer growth and found that it interferes with two key cellular processes: glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that produces energy in the absence of oxygen, while mitochondrial respiration is a process that generates energy in the presence of oxygen. The researchers found that taurine inhibits glycolysis and enhances mitochondrial respiration, which ultimately leads to the death of cancer cells.
These findings have important implications for the development of new treatments for ovarian cancer. Currently, the standard treatment for ovarian cancer involves surgery and chemotherapy, which can be highly invasive and have significant side effects. Taurine, on the other hand, is a natural and non-toxic dietary supplement that has been shown to be effective in suppressing ovarian cancer growth.
The authors note that further research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms behind the anti-tumor effects of taurine and to optimize its use as a treatment. Additionally, more studies are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of taurine supplementation in humans. However, the potential for a non-invasive, non-toxic treatment option that can be used in combination with standard therapies is an exciting development in the fight against ovarian cancer.
Key takeaways from the study:
- The study investigated the effects of taurine on the growth of ovarian cancer cells.
- Taurine significantly inhibited the growth of ovarian cancer cells and induced cell death.
- Taurine altered the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and energy metabolism.
- Taurine inhibits glycolysis and enhances mitochondrial respiration, ultimately leading to the death of cancer cells.
- Taurine has potential as a non-invasive, non-toxic dietary supplement for suppressing ovarian cancer growth.
- Further research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms behind the anti-tumor effects of taurine and to optimize its use as a treatment.
- More studies are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of taurine supplementation in humans.
The findings of this study have significant implications for public health, as ovarian cancer is a deadly disease that affects thousands of women each year. While current treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy can be effective, they often come with a host of side effects and do not guarantee long-term survival. The discovery of a safe and effective dietary supplement that can be used in combination with standard therapies could greatly improve the quality of life and prognosis for patients with ovarian cancer.
The researchers also investigated the underlying mechanisms by which taurine suppresses ovarian cancer growth. They found that taurine interferes with two key cellular processes: glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that produces energy in the absence of oxygen, while mitochondrial respiration is a process that generates energy in the presence of oxygen. The researchers found that taurine inhibits glycolysis and enhances mitochondrial respiration, which ultimately leads to the death of cancer cells.
These findings have important implications for the development of new treatments for ovarian cancer. Currently, the standard treatment for ovarian cancer involves surgery and chemotherapy, which can be highly invasive and have significant side effects. Taurine, on the other hand, is a natural and non-toxic dietary supplement that has been shown to be effective in suppressing ovarian cancer growth.
The researchers are now planning to investigate the effects of taurine on other types of cancer, as well as the potential synergistic effects of combining taurine with other cancer treatments. The study provides a strong foundation for future research on the use of taurine as a therapeutic agent for cancer, which could have a significant impact on public health.
In conclusion, the study by Centeno and colleagues provides important new insights into the potential of taurine as a novel therapeutic approach for ovarian cancer. As further research is conducted, it is hoped that taurine will become an important tool in the fight against this deadly disease. The findings of this study have significant implications for public health, as ovarian cancer is a deadly disease that affects thousands of women each year. While current treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy can be effective, they often come with a host of side effects and do not guarantee long-term survival. The discovery of a safe and effective dietary supplement that can be used in combination with standard therapies could greatly improve the quality of life and prognosis for patients with ovarian cancer.
It is important to note that further research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms behind the anti-tumor effects of taurine and to optimize its use as a treatment. Additionally, more studies are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of taurine supplementation in humans. However, the results of this study are promising, suggesting that taurine could be a potential therapeutic option for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
In addition to its potential use as a cancer treatment, taurine has many other health benefits. It is commonly found in energy drinks and other dietary supplements, where it is touted for its ability to improve athletic performance, enhance cognitive function, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of taurine on human health and its long-term safety.
The study's lead author, Marcin Iwanicki, noted that the team's findings are particularly significant given the lack of effective treatment options for ovarian cancer. "Ovarian cancer is a particularly challenging disease to treat, and we need new and innovative approaches to combat it," he said. "Our study suggests that taurine could be a promising new avenue for research and treatment, and we are excited to explore its potential further."
Overall, the study provides important new insights into the potential of taurine as a therapeutic agent for cancer. While further research is necessary to fully understand its mechanisms of action and safety, the findings offer hope for the development of new, non-toxic treatments for ovarian and other types of cancer.
source : The Dietary Supplement Taurine Suppresses Ovarian Cancer Growth : Daniel Centeno, Sadaf Farsinejad, Elena Kochetkova, Tatiana Volpari, Agnieszka Klupczynska-Gabryszak, Douglas Kung, Teagan Polotaye, Emily Hyde, Tonja Pavlovic, Sarah Alshehri, William Sullivan, Szymon Plewa, Frederick J Monsma Jr, Jan Matysiak, Mikolaj Zaborowski, Analisa Difeo, Laura A. Martin, Erik Norberg, View ORCID ProfileMarcin Iwanicki